Power + Thermal Layer: Why Cold Matters
Cold climates offer cooling advantages — but don’t hallucinate this into “free energy.”
Compute Cooling
Advantages
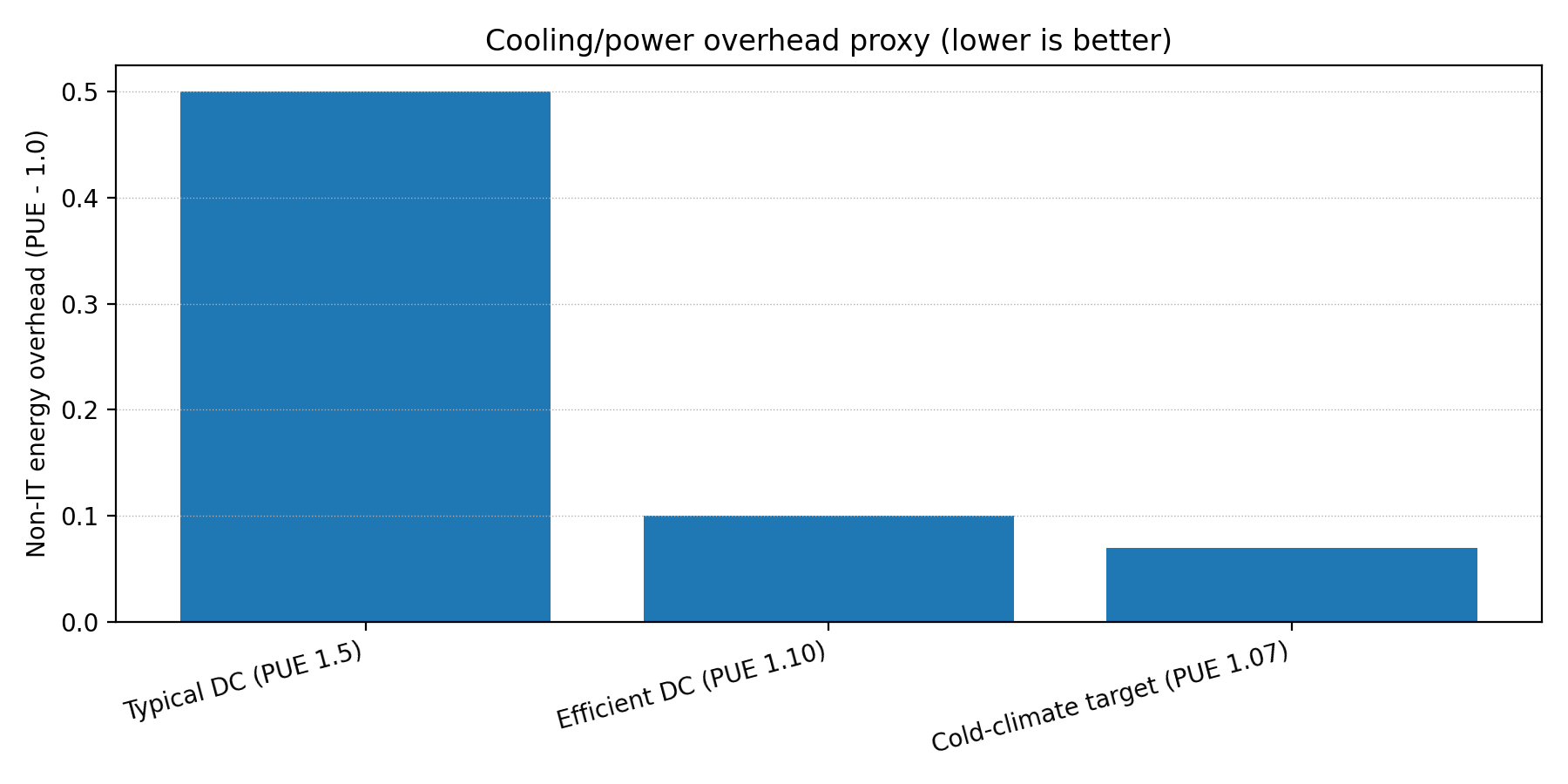
- More hours of economized cooling — “Free cooling” from cold ambient air
- Lower PUE — Power Usage Effectiveness improves with reduced HVAC load
- Stable heat rejection — Consistent cold sink year-round
Constraints
You still need:
| Requirement | Why |
|---|---|
| Reliable generation + transmission | Grid stability in remote locations |
| Redundancy (N+1 / 2N) | Critical nodes cannot fail |
| Humidity control | Cold air is dry → ESD risk, material constraints |
Fab Cooling (Semiconductors)
Advanced fabs are dominated by cleanroom HVAC, filtration, and strict temperature/humidity stability.
Cold Climate Benefits
- Reduced lift — Less work per unit heat removed (chiller efficiency)
- More stable heat rejection — Consistent condenser performance
Cold Climate Constraints
- Tight internal control still required
- Per-wafer water requirements remain substantial
- Cleanroom HVAC recirculation dominates energy
Don’t confuse “cool air” with “cheap fab.”
Water Requirements
Semiconductor manufacturing consumes large volumes of ultrapure water (UPW):
| Process | Water Impact |
|---|---|
| Wafer cleaning | High-purity rinse cycles |
| Chemical preparation | Dilution and mixing |
| Cooling | Process and facility cooling |
Winter operations: Water intake and treatment must handle freeze/thaw cycles.
Waste Heat Reuse
In cold regions, waste heat from data centers is a resource:
Data Center Heat Output ↓ Heat Exchanger ↓ District Heating Grid ↓ Community Buildings / GreenhousesThis converts “cooling cost” into “community heat,” improving overall system economics.
Key Metrics
| Metric | Target |
|---|---|
| PUE | < 1.2 (with free cooling) |
| WUE | Minimize, track year-round |
| Heat recovery | > 50% to district heating |